How Do LCFS Credits Work? Breaking Down the Low Carbon Fuel Standard Credit System
April 12, 2024
A low carbon fuel standard (LCFS) is an energy rebate program that offers credit-based incentives for the use of electric and low-carbon vehicles. This opens the door to additional revenue for EV fleet owners.
This article explains how LCFS credits work to help you maximize your earnings with your state’s LCFS program.
Background: How Low Carbon Fuel Standards Work

Understanding how LCFS credit systems works can be a major advantage in maximizing your credit generation, and the revenue that comes from your LCFS credits.
Learn more: What Are Energy Rebate Programs?
Below, we’ll review each step of the LCFS credit generation process.
1. Setting Emission Benchmarks with Carbon Intensity Scores
While each LCFS program has its own specific regulations and goals, all programs use carbon intensity scores to measure the environmental impact of a fuel. CI scores are determined by a fuel’s carbon emissions throughout its lifecycle, including extraction, refinement, generation, and usage. A higher CI score represents greater environmental impacts, while eco-friendly fuels have a lower CI score – and in some cases, like electricity, a negative CI score.
LCFS programs set CI benchmarks that decrease annually, pushing fuel suppliers towards lower emissions and allowing users of low CI fuels to generate credits.
2. Credit Generation
In most LCFS programs, using vehicles with fuels below the annual CI benchmark generates credits. These fuels typically include electricity, biodiesel, ethanol, and hydrogen. For fleet owners, this means that every gallon of gasoline or diesel replaced with alternative fuels directly contributes to their credit tally. The lower the CI of the fuel, the more credits generated per unit of energy consumed. Electricity has a negative CI score in most LCFS programs, offering EV owners faster credit generation than some other low-carbon fuels.
In some energy rebate programs, like Oregon’s Clean Fuel Program, only fuel providers — such as importers and producers of fossil fuel, owners of charging stations, and natural gas dispensers — are eligible to generate credits. In these cases, owners of electric vehicle charging stations can take advantage of rebate opportunities, rather than owners of electric vehicles.
Every LCFS program varies in its eligible fuels and vehicles. In some states, including California, Oregon, and Washington, electric forklifts are a prolific source of credits. Some programs are even considering adding aviation fuels to their lists. EV fleet owners should be aware of all of their state’s eligibility criteria to ensure they’re generating as many credits as possible.
3. Credit Calculation and Value
Credits are sold to fuel producers – including importers, refiners, and wholesalers – who fail to meet CI benchmarks and must purchase LCFS credits to offset their deficits. The value of credits is calculated based on the demand from fuel suppliers (i.e. how many credits are needed to offset the total amount of deficits) and the availability of credits. As CI benchmarks get progressively lower, the demand for credits increases. The value of credits fluctuates based on the supply and demand of the trading market, oftentimes with large fluctuations in a single day. For this reason, many fuel producers only purchase credits in bulk, minimizing the volatility of credit value.
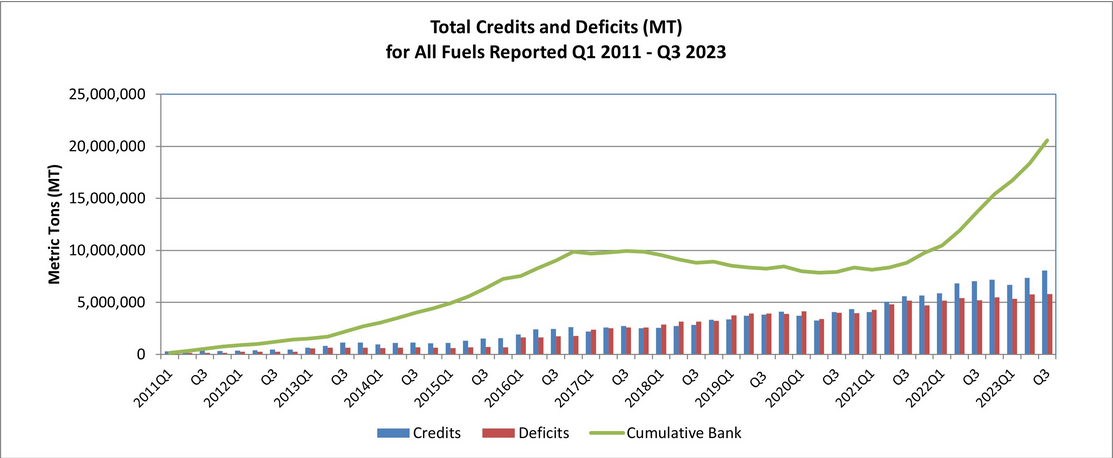
Figure 1. The total credits and deficits produced in California’s LCFS program over the last 13 years since its implementation.
Source: California Air Resource Board
Getting the Most Out of Your LCFS Credits
A key tool in maximizing the value of your credits is partnering with third-party credit aggregators like Smart Charging Technologies (SCT) who can monitor the credit market and sell your credits in bulk to ensure the highest price. Additionally, SCT offers in-person audits that make sure your fleet is generating credits from every eligible piece of equipment based on your program’s state-specific criteria.
SCT specializes in managing the complexities of energy rebate programs across the US and Canada for both fleet owners and owners of electric vehicle charging stations. LCFS programs are currently in place in:
- California
- Oregon
- Washington
- Canada
- New Mexico
A growing number of US states are drafting legislation to create their own LCFS programs. Stay up-to-date with your state’s legislation and potential rebate opportunities: New LCFS Legislation Across the US.
Contact us today to learn more about how SCT can help you enroll in your state's energy rebate program and begin generating credits today.
Related Posts